A home loan is a financial obligation instrument, secured by the collateral of defined real estate property, that the debtor is required to pay back with an established set of payments. Home mortgages are likewise called "liens versus residential or commercial property" or "claims on property." With a fixed-rate mortgage, the debtor pays the same rates of interest for the life of the loan.
Individuals and companies utilize home mortgages to make big property purchases without paying the whole purchase cost up front. Over several years, the debtor pays back the loan, plus interest, up until she or he owns the home free and clear. Mortgages are likewise referred to as "liens versus residential or commercial property" or "claims on home." If the customer stops paying the home loan, the loan provider can foreclose.
In a property home mortgage, a property buyer pledges their house to the bank or other kind of lender, which has a claim on the home ought to the homebuyer default on paying the mortgage. When it comes to a foreclosure, the lending institution may kick out the home's tenants and offer the home, utilizing the income from the sale to clear the mortgage debt.
The most popular home loans are a 30-year fixed and a 15-year fixed. Some home mortgages can be as brief as five years; some can be 40 years or longer. Stretching payments over more years reduces the month-to-month payment but increases the quantity of interest to pay. With a fixed-rate home loan, the customer pays the same rate of interest for the life of the loan.
If market interest rates increase, the debtor's payment does not alter. If rate of interest drop substantially, the customer might have the ability to secure that lower rate by re-financing the home loan. A fixed-rate mortgage is also called a "conventional" home mortgage. With an adjustable-rate home mortgage (ARM), the rates of interest is repaired for an initial term then varies with market interest rates.
If interest rates increase later, the borrower might not have the ability to afford the higher regular monthly payments. Rates of interest could also reduce, making an ARM more economical. In either case, the regular monthly payments are unpredictable after the preliminary term. Home loans are utilized by individuals and organizations to make big real estate purchases without paying the entire purchase cost up front.
Examine This Report on How Do Assumable Mortgages Work
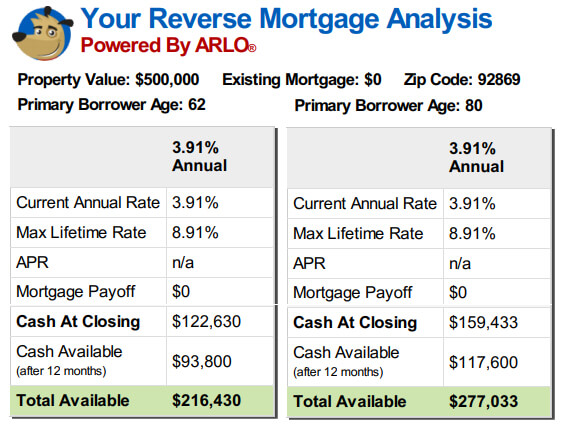
Lots of house owners got into monetary trouble with these types of home mortgages during the real estate bubble of the early 2000s. Most home loans utilized to buy a house are forward mortgages. A reverse home mortgage is for homeowners 62 or older who want to convert part of the equity in their homes into cash.
The entire loan balance becomes due and payable when the customer dies, moves away completely, or offers the home. Among major banks using home loan are Wells Fargo, JPMorgan Chase, and Bank of America. Banks utilized to be virtually the only source of mortgages (how do arm mortgages work). Today a growing share of the loan provider market includes non-banks such as Quicken Loans, loanDepot, SoFi, Calber House Loans, and United Wholesale Home Loan.
These tools can likewise assist determine the overall cost of interest over the life of the home mortgage, to offer you a clearer concept of what a residential or commercial property will really cost. how do points work in mortgages. The home mortgage servicer might likewise set up an escrow account, aka a take account, to pay specific property-related costs. The cash that goes into the account comes from a portion of the month-to-month mortgage payment.
Customer Financial Defense Bureau - how does chapter 13 work with mortgages. Home loans, possibly more than any other loans, featured a lot of variables, beginning with what should be paid back and when. Homebuyers need to deal with a home loan specialist to get the finest deal on what may be one of the most significant investments of their lives.
When you buy a house, you might hear a bit of industry terminology Click for info you're not familiar with. We've produced an easy-to-understand directory site of the most common home loan terms. Part of each monthly home mortgage payment will approach paying interest to your loan provider, while another part goes toward paying down your loan balance (also called your loan's principal).
Throughout the earlier years, a greater part of your payment approaches interest. As time goes on, more of your payment approaches paying for the balance of your loan. The deposit is the cash you pay in advance to purchase a house. In a lot of cases, you need to put money down to get a home mortgage.
The 5-Minute Rule for How Do Home Interest Mortgages Work
For example, traditional loans require just 3% down, however you'll need to pay a monthly fee (referred to as personal home mortgage insurance) to compensate for the small down payment. On the other hand, if you put 20% down, you 'd likely get a much better interest rate, and you wouldn't need to spend for private home mortgage insurance coverage.
Part of owning a home is paying for real estate tax and property owners insurance. To make it simple for you, loan providers set up an escrow account to pay these expenses. Your escrow account is managed by your lender and works sort of like a monitoring account. Nobody makes interest on the funds held there, but the account is utilized to collect money so your lending institution can send out payments for your taxes and insurance https://franciscolwpc506.tumblr.com/post/634100453421056000/an-unbiased-view-of-how-do-rehab-mortgages-work coverage on your behalf.
Not all mortgages include an escrow account. If your loan doesn't have one, you have to pay your real estate tax and property owners insurance coverage expenses yourself. However, most lenders provide this option due to the fact that it allows them to make certain the property tax and insurance costs earn money. If your down payment is less than 20%, an escrow account is required.
Keep in mind that the amount of money you need in your escrow account is reliant on how much your insurance coverage and property taxes are each year. And since these costs may change year to year, your escrow payment will alter, too. That indicates your month-to-month home mortgage payment may increase or decrease.
There are two kinds of mortgage interest rates: repaired rates and adjustable rates. Repaired rate of interest remain the very same for the whole length of your home loan. If you have a 30-year fixed-rate loan with a 4% rate of interest, you'll pay 4% interest until you pay off or re-finance your loan.
Adjustable rates are rate of interest that alter based upon the market. Most adjustable rate mortgages begin with a set interest rate duration, which typically lasts 5, 7 or ten years. Throughout this time, your rate of interest remains the exact same. After your fixed rate of interest duration ends, your interest rate changes up or down once each year, according to the marketplace.
Get This Report about How Does Securitization Of Mortgages Work
ARMs are ideal for some debtors. If you plan to move or refinance before the end of your fixed-rate duration, an adjustable rate mortgage can give you access to lower rates of interest than you 'd typically find with a fixed-rate loan. The loan servicer is the business that's in charge of supplying month-to-month mortgage statements, processing payments, managing your escrow account and reacting to your inquiries.
Lenders may offer the maintenance rights of your loan and you may not get to choose who services your loan. There are many types of mortgage loans. Each includes various requirements, interest rates and advantages. Here are some of the most typical types you may find out about when you're using for a mortgage.